
Biotech Act : precaution sacrificed in the name of innovation?
In a recent proposal for regulations claiming to “strengthen the biotechnology and biomanufacturing sectors”, the European Commission wants to see these sectors governed by a policy that “balance innovation with safety, equity and environmental protection”. However, the text mainly aims to promote industrial competitiveness and attractiveness to investors. It provides for faster authorisation procedures for “biotechnology products”, a lighter regulatory framework and prioritisation of so-called “strategic” projects in order to reduce time to market.

What “discussion” procedures are imposed on European legislators?
Since July 2023, EU institutions have been engaged in discussions on the proposal to deregulate many GMOs. These discussions follow an established procedure of negotiations between the Council of the European Union, the European Parliament and the European Commission. Complex but logical, this procedure can sometimes confuse those who follow it. Inf’OGM helps you see things more clearly.

French government in favour of deregulating many GMOs
On 19 December 2025, the French government came out in favour of deregulating GMOs obtained using new techniques of genetic modification (NGT). Having previously abstained, it has, according to our information, changed its position following a commitment made by the European Commission. This commitment, which has not yet been made public but which Inf’OGM has been able to read, does not, however, add anything to the provisional text proposed to deregulate GMOs. France’s position has enabled a qualified majority of Member States to be reached on a text that, furthermore, does not provide for any risk assessment of GMOs obtained using new techniques and classified in category 1, any labelling or traceability of these GMOs, or any environmental monitoring.
The deregulation of GMO microorganisms is underway
A proposal for a directive made by the European Commission on 16 December 2025 calls on Member States and the European Parliament to deregulate the marketing of genetically modified bacteria, yeasts, viruses and other micro-organisms, including transgenics. According to the Commission, the aim would be to allow companies to market these GMO microorganisms (GMMs) under lighter or even no rules. This would involve an “adapted” health and environmental risk assessment, an end to traceability, an end to environmental monitoring… Following the plants, the deregulation of GMOs is therefore continuing, this time with microorganisms, with perhaps the animals next in line in 2026.

GMOs, seeds, pesticides, transparency… European law under attack!
In less than two weeks, between 10 and 19 December, 2025 ended with a rather unprecedented offensive by the European Union authorities against several European texts protecting the environment, health and citizens’ rights. GMOs, pesticides, seeds, corporate responsibility… everything is being called into question in order to “simplify” life for businesses in Europe. Faced with this frenetic pace, Inf’OGM continues its watchdog work, which is essential for public debate, the proper functioning of democracy and the protection of life, by providing accurate, rigorous and reliable information.

Agricultural biodiversity at risk with new seed regulation
On 10 December 2025, the Council of the European Union approved a mandate to begin negotiations with the European Parliament on a new seed regulation. Many civil society organisations have criticised the draft regulation for failing to protect small and medium-sized breeders, seed producers and farmers. They are calling for a diverse seed market, the implementation of farmers’ rights to seeds and guaranteed access to varieties suited to their farming systems.

Qualified majority in the Council of the European Union to deregulate numerous GMOs
On Friday 19 December, the Member States meeting within the Council of the European Union reached a qualified majority agreement on a text to deregulate many GMOs. This text, negotiated two weeks earlier between representatives of the European Commission, the European Parliament and the Council, proposing broad deregulation of GMOs obtained through new techniques of genetic modification, has finally convinced a sufficient majority of States. The European Parliament is now due to consider it in January 2026.

The majority of micro-organisms modified by NGTs are detectable
In 2025, the European network of GMO laboratories (ENGL) published a report written by several of its experts on the detection and identification of genetically modified microorganisms using new techniques in the food and feed industry. According to this report, the vast majority of these micro-organisms are detectable and identifiable. However, “in somecases”, with the processes currently available, very small genetic modifications can be more complicated, or even impossible, to detect and differentiate from those that can occur without technical intervention on the genome.
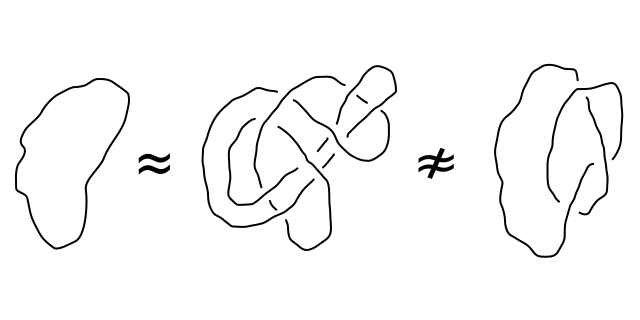
GMO/non-GMO equivalence: the Commission turns “certain cases” into a general rule
The proposal to deregulate some of the GMO plants made by the European Commission in July 2023 is based in particular on the assumption that new techniques of genetic modification can produce organisms with modifications that could also be obtained using so-called “conventional” methods. To make this claim, the European Commission uses a subtle but decisive semantic abuse in its proposal…

NGT regulations: trilogue of the deaf under pressure from Denmark
Negotiations on the future European regulation on new genetic modification techniques have been focusing on two sensitive issues for several months: patentability and sustainability. Keen to conclude the dossier before the end of the year, the Danish Presidency is stepping up efforts to find a compromise, at the risk of neglecting issues that are of particular concern to small and medium-sized breeders and farmers. Denmark will seek an agreement this week, having already threatened to freeze discussions and refer the text back to the European Parliament for a second reading.
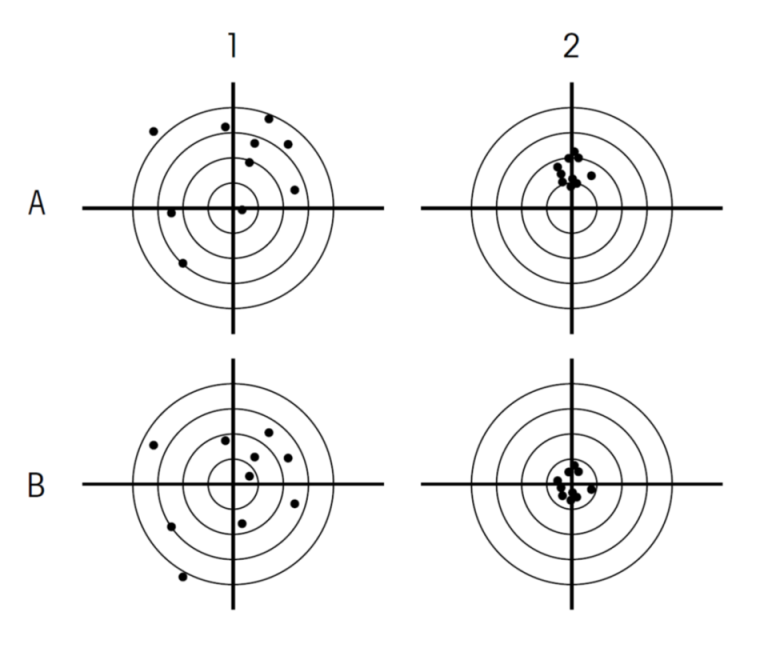
Directed, targeted, precise mutagenesis… Are these adjectives misleading?
Being precise, targeting and achieving one’s goal, directing a mutagenesis… these are adjectives that convey a sense of control and precision. However, on closer inspection, these adjectives mean nothing in a legal text. Because, in the European Commission’s proposal to deregulate a number of GMOs, they are not accompanied by their corollaries: targeted where? Precise to what degree? Directed by what or by whom?

Consumer associations call for continued labelling and traceability of GMOs
On 14 October 2025, eight consumer associations from various EU Member States published an opinion calling on European institutions to maintain GMO labelling to enable European consumers to make informed choices about their food.

