Despite pitfalls and dangers, gene drive is still on the table
In September 2025, the French Academy of Sciences published a summary of the risks it identified as being associated with gene drive. This technique, which emerged around ten years ago, presents a variety of potential dangers and is uncontrollable. As a result, it has not yet been deployed in the wild. However, the current context is very conducive to its development and the precautionary principle is under threat.

“Animal proteins” without animals
Animal proteins without animalsMilk proteins without cows, fish without fish, meat without animals and even egg proteins without eggs or chickens: welcome to the realm of “precision fermentation” for our future food. Three start-ups in the sector have obtained approval for their milk-free milk proteins from the US health authorities, enabling them to sell them to food manufacturers.The industry and certain institutions are presenting these innovations as a step forward in reducing the carbon impact of livestock farming and meeting the food needs of human populations. Above all, it is a promising market: these “advances” are already attracting investors.

Bioengineered poplars to save the climate?
A few months ago, Living Carbon, a US start-up, announced that it had developed and planted genetically modified poplar trees in 2023. These trees are said to absorb more quickly carbon dioxide, one of the greenhouse gases whose current accumulation in the atmosphere and oceans is causing problems for the Earth’s climate. As part of this program, Living Carbon is acquiring carbon credits to finance its work. The aim is to reduce the photorespiration of poplar and pine plants. What is photorespiration? What would be the ecological repercussions of this modification of photosynthesis?

Limagrain, a “cooperative” that has always bet on GMOs
Behind its label as an agricultural cooperative from Auvergne (France), Limagrain is now a global player in GMOs. The Group has been promoting GMOs for many years. Last March, its CEO, Sébastien Chauffaut, was optimistic about the forthcoming deregulation of GMOs/NGTs, which he hopes to market from 2029. Here’s a look at Limagrain’s GMO strategy, combining state privilege and lobbying.

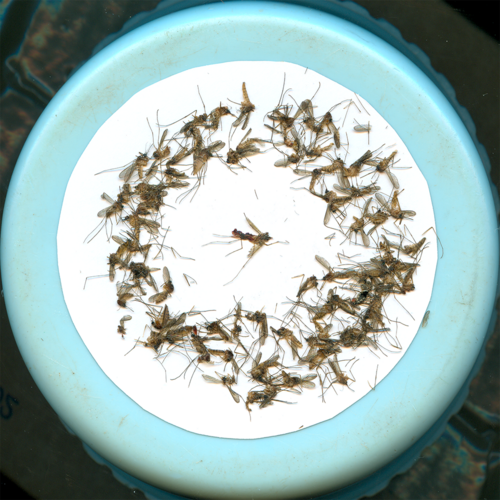
Male mosquitoes genetically modified to produce poison
Mosquitoes carry pathogens that cause diseases such as malaria and dengue fever, and are therefore known as vector-borne diseases. As part of the fight against these mosquitoes, researchers at Macquarie University (Australia) are considering a new genetic strategy. The idea is to genetically modify male mosquitoes so that their sperm produce molecules that will poison female mosquitoes.
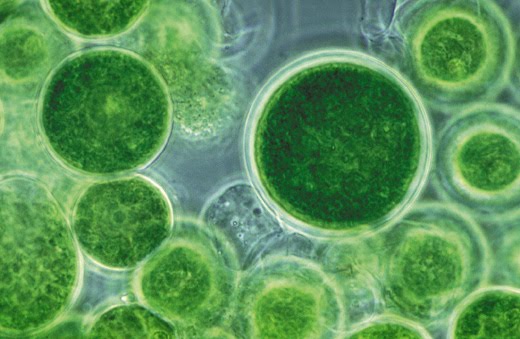
Object of all desire, do GM algae really exist?
Algae are the surprise guest in the European Commission’s deregulation proposal. How are these organisms used by the industry? In which countries are they produced? And above all, what genetic modifications are being made for which comercialisation? This overview is of importance because, according to the European Commission, their deregulation – like that of other plant GMOs – would be justified by the “evidence […] on the safety” of these GMOs. However, these GM algae do not exist, as the technical protocols are not yet mastered…

Through its silence, the European Commission has been keeping Mon810 maize authorised since 15 years
Mon810 maize is the only transgenic GM plant authorized for commercial cultivation in the European Union. This authorization was initially granted, via France, almost 30 years ago, in 1998, for an initial period of 10 years. A renewal application was submitted in 2007. Since then, no decision has been taken by the European authorities. How this maize, which authorization theoretically expired in 2008, can still be grown legally in Europe? Simply because European law accepts that, as long as the European Commission has not responded to a request for renewal, the initial authorization remains valid. To date, it’s been 15 years that the Commission fails to respond to Bayer/Monsanto’s request.

25 years later, insecticidal GMOs face insect resistance
43 detections of insects having acquired resistance to the Bt proteins supposed to kill them were listed in a scientific article in 2023. 43 cases out of 73 studied, i.e. more than half. For the authors of the article, the use of insecticidal GMOs has been crowned with success, as in several cases it has made it possible to reduce or even eradicate local pests. But failures also occurred due to resistance. The authors believe that the future lies in a combination of technologies, among which is RNA interference.

In Spain, are some insects beginning to resist GM maize?
For almost 15 years, European and French experts have been recommending that Bayer improve environmental monitoring of commercial Mon810 corn crops in Spain and Portugal. This improvement is necessary, they say, to prevent target insects such as the European corn borer and sesamia from developing resistance to the insecticide produced by this transgenic corn. But year after year, Bayer only partially responds to these requests. Yet concerns are becoming increasingly serious and concrete, as demonstrated by the latest EFSA opinion, published in August 2024.

Catalonia: GMO Clearfield rapeseeds do not have better yields
In Spain, the public agronomy institute Irta regularly carries out evaluations of several varieties of rapeseed. Recently, they introduced into their evaluation some Clearfield rapeseed varieties, herbicide tolerant varieties modified via in vitro mutagenesis. Result: these GMOs, grown commercially in Europe outside the legal framework, do not have better yields than their conventional counterparts.


