
Will satellites save agriculture?
“How can we feed 10 billion people in 2050 with limited natural resources? To address this challenge, agritech start-ups are capitalising on the latest research findings to offer disruptive innovations and provide more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions” . This is how agritech is presented by BPI France, the French public investment bank. Once again, we see the famous promise to feed the world. To achieve this goal, we need to innovate, invest, digitise, robotise…

Illegal cultivation of GM soybeans in Tunisia revealed by DNA tests
Presented as a response to the feed crisis, a new crop is quietly taking root in Tunisian fields. Behind the soybeans, genetically modified seeds are being introduced without regulation and amid total institutional silence.

When algorithms decide on the genetic modification of living organisms
For many years now, multinationals have been collecting an increasing amount of genetic, proteic sequences and epigenetic informations. They are reducing living organisms to data compiled in digital databases. Using “artificial intelligence” algorithms, they claim to have the tools to determine which genetic modifications will produce a given new characteristic. In a society where genetic modification techniques and patents are intimately linked, these algorithms will above all accelerate the claim to own living organisms.
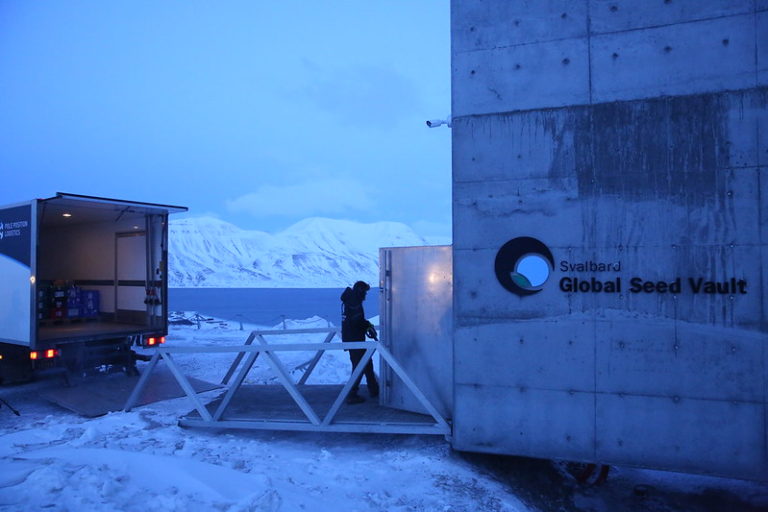

Pro-GMO multinationals indirectly manage the Svalbard seed bank
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault (Svalbard, Norway), often nicknamed the “seed vault”, plays a special role in preserving genetic biodiversity. Its main mission, focused on the long-term conservation of seed samples, is officially to preserve the diversity of plant genetic resources and ensure their accessibility in the event of disasters. However, a closer look at how it works reveals the considerable influence and interests of pro-GMO players in its governance. Who will really benefit from Svalbard, the multinationals or the farmers?

Through its silence, the European Commission has been keeping Mon810 maize authorised since 15 years
Mon810 maize is the only transgenic GM plant authorized for commercial cultivation in the European Union. This authorization was initially granted, via France, almost 30 years ago, in 1998, for an initial period of 10 years. A renewal application was submitted in 2007. Since then, no decision has been taken by the European authorities. How this maize, which authorization theoretically expired in 2008, can still be grown legally in Europe? Simply because European law accepts that, as long as the European Commission has not responded to a request for renewal, the initial authorization remains valid. To date, it’s been 15 years that the Commission fails to respond to Bayer/Monsanto’s request.

GreenLight Biosciences or the RNA at every level
After genetic sequences and DNA, here comes RNA, the new flagship molecule in biotechnology that is supposed to solve agricultural and health problems. Companies in this field are flourishing. Among them is GreenLight Biosciences, a company that was on the verge of bankruptcy when it was bought by the investment fund Fall Line Capital.

In Spain, are some insects beginning to resist GM maize?
For almost 15 years, European and French experts have been recommending that Bayer improve environmental monitoring of commercial Mon810 corn crops in Spain and Portugal. This improvement is necessary, they say, to prevent target insects such as the European corn borer and sesamia from developing resistance to the insecticide produced by this transgenic corn. But year after year, Bayer only partially responds to these requests. Yet concerns are becoming increasingly serious and concrete, as demonstrated by the latest EFSA opinion, published in August 2024.
Journal
Patents on NGTs, between disputes and desire: the case of Crispr-Cas 9

Journal
Seed patents: the industry’s great manoeuvres


