Nanoparticles galore in pesticides
A report by ANSES, published last April, proposes to increase vigilance regarding the use of nanopesticides. These nanometric molecules are highly volatile, which considerably increases their potential for dissemination and contamination, as well as their potential toxic effects on the body. The problem is that not only is their sale unregulated in Europe, but the regulations do not provide for their detection.
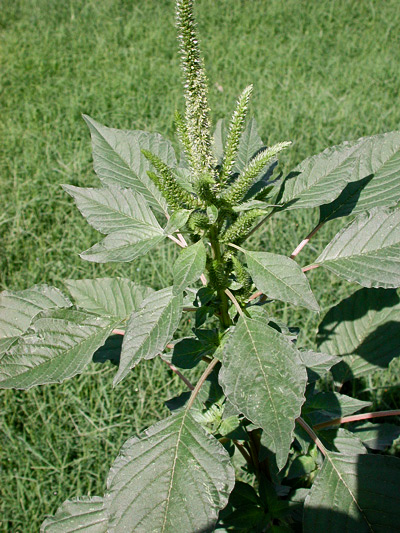

Palmer amaranth, an extremely invasive weed, arrives in France
As soon as farmers began using herbicides on a large scale, weeds tolerant to these substances appeared. This is a simple biological phenomenon: living organisms are constantly adapting. The cultivation of genetically modified plants has accelerated this development of tolerance, which has significant agricultural and economic consequences. In France, a highly invasive weed known as Palmer amaranth, which is resistant to several types of herbicides, could soon take hold. This is the fear expressed by ANSES in a report published in December 2025.

What “discussion” procedures are imposed on European legislators?
Since July 2023, EU institutions have been engaged in discussions on the proposal to deregulate many GMOs. These discussions follow an established procedure of negotiations between the Council of the European Union, the European Parliament and the European Commission. Complex but logical, this procedure can sometimes confuse those who follow it. Inf’OGM helps you see things more clearly.

Patents and NGTs: the singular position of Germany’s main agricultural union
While the deregulation of GMOs obtained through new genetic modification techniques (GMOs/NGTs) is currently under review, the issue of patents continues to provoke contrasting positions within European agricultural organisations. In this context, the position of the Deutscher Bauernverband (DBV), Germany’s main agricultural union, is particularly noteworthy. While in favour of the use of these NGTs, it nevertheless warns of the risks associated with patents. This is an original position among European agricultural organisations.

MEPs approached by industry to deregulate GMOs/NGTs
Since the European Commission submitted its proposal to deregulate almost all GMOs in 2023, multinational seed companies and lobbyists have been busy lobbying European institutions to support this proposal. Companies and civil society organizations can request meetings with MEPs. These meetings are listed, at least in part, on the Parliament’s website. In this article, Inf’OGM shows that supporters of GMO deregulation had 59 meetings, compared to 23 for opponents.

French government in favour of deregulating many GMOs
On 19 December 2025, the French government came out in favour of deregulating GMOs obtained using new techniques of genetic modification (NGT). Having previously abstained, it has, according to our information, changed its position following a commitment made by the European Commission. This commitment, which has not yet been made public but which Inf’OGM has been able to read, does not, however, add anything to the provisional text proposed to deregulate GMOs. France’s position has enabled a qualified majority of Member States to be reached on a text that, furthermore, does not provide for any risk assessment of GMOs obtained using new techniques and classified in category 1, any labelling or traceability of these GMOs, or any environmental monitoring.
The deregulation of GMO microorganisms is underway
A proposal for a directive made by the European Commission on 16 December 2025 calls on Member States and the European Parliament to deregulate the marketing of genetically modified bacteria, yeasts, viruses and other micro-organisms, including transgenics. According to the Commission, the aim would be to allow companies to market these GMO microorganisms (GMMs) under lighter or even no rules. This would involve an “adapted” health and environmental risk assessment, an end to traceability, an end to environmental monitoring… Following the plants, the deregulation of GMOs is therefore continuing, this time with microorganisms, with perhaps the animals next in line in 2026.

GMOs, seeds, pesticides, transparency… European law under attack!
In less than two weeks, between 10 and 19 December, 2025 ended with a rather unprecedented offensive by the European Union authorities against several European texts protecting the environment, health and citizens’ rights. GMOs, pesticides, seeds, corporate responsibility… everything is being called into question in order to “simplify” life for businesses in Europe. Faced with this frenetic pace, Inf’OGM continues its watchdog work, which is essential for public debate, the proper functioning of democracy and the protection of life, by providing accurate, rigorous and reliable information.

The Council of the EU wants to maintain the patentability of GMOs/NGTs
On 19 December 2025, in a still provisional text, the Council of the European Union maintained the patentability of GMOs derived from new genetic techniques (NGT). To this end, it relied on existing law and called for voluntary, but non-binding, commitments, without taking into account the impact on farmers and small seed producers. This text still needs to be validated, amended or rejected by the European Parliament, which had voted against these patents in 2024 and will have to take a position in 2026 without being able to propose new amendments.

Agricultural biodiversity at risk with new seed regulation
On 10 December 2025, the Council of the European Union approved a mandate to begin negotiations with the European Parliament on a new seed regulation. Many civil society organisations have criticised the draft regulation for failing to protect small and medium-sized breeders, seed producers and farmers. They are calling for a diverse seed market, the implementation of farmers’ rights to seeds and guaranteed access to varieties suited to their farming systems.

New GMOs to produce medicines tested in Spain
Near Valencia (Spain), in Polinyà del Xúquer, a trial of genetically modified tobacco to produce a molecule of therapeutic interest has been authorised. This tobacco has been modified using genetic modification techniques presented as new (NGT). The two partners in charge of the trial, the company MadeInPlant and the agricultural union AVA, declared the trial in December 2024, in accordance with Directive 2001/18 governing GMOs, even though they claim that this tobacco is not a GMO but an NTG plant.

Qualified majority in the Council of the European Union to deregulate numerous GMOs
On Friday 19 December, the Member States meeting within the Council of the European Union reached a qualified majority agreement on a text to deregulate many GMOs. This text, negotiated two weeks earlier between representatives of the European Commission, the European Parliament and the Council, proposing broad deregulation of GMOs obtained through new techniques of genetic modification, has finally convinced a sufficient majority of States. The European Parliament is now due to consider it in January 2026.

