Pairwise shapes the food of the future with NGT
While the European Commission is attempting to deregulate new genome modification techniques (NGT), the US company Pairwise is multiplying its “partnerships” combining the Crispr/Cas tool and its Fulcrum platform. Concluded with both private and public players, these agreements anticipate the landscape following the potential deregulation of NGT. They will also influence the conditions for the dissemination of NGT and the arrival of “Pairwise-type” products on our plates.

Origin of Covid-19: laboratory leak is the most likely scenario
A Covid-19 epidemic (acronym for ‘coronavirus disease 2019’) was officially declared in January 2020 in the city of Wuhan, then quickly turned into a pandemic spreading throughout the world. The rapid spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus (for ‘Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome’), responsible for this pandemic, led to lockdowns being imposed on everyone, regardless of age group or susceptibility to the disease. It has disrupted the lives of billions of people. But where did the virus come from? This three-part article aims to describe what is known about the origin of this virus and why it should matter to us, here and now. All those involved in this pandemic story are undoubtedly hiding part of the truth.
In the first part, we explain the issue and why it may be of interest to us, even after the pandemic is over, and describe its main players. In the second part, we will review the history of this pandemic. In the third part, we will give the opinions of various institutions on its origin.

Limagrain, a “cooperative” that has always bet on GMOs
Behind its label as an agricultural cooperative from Auvergne (France), Limagrain is now a global player in GMOs. The Group has been promoting GMOs for many years. Last March, its CEO, Sébastien Chauffaut, was optimistic about the forthcoming deregulation of GMOs/NGTs, which he hopes to market from 2029. Here’s a look at Limagrain’s GMO strategy, combining state privilege and lobbying.
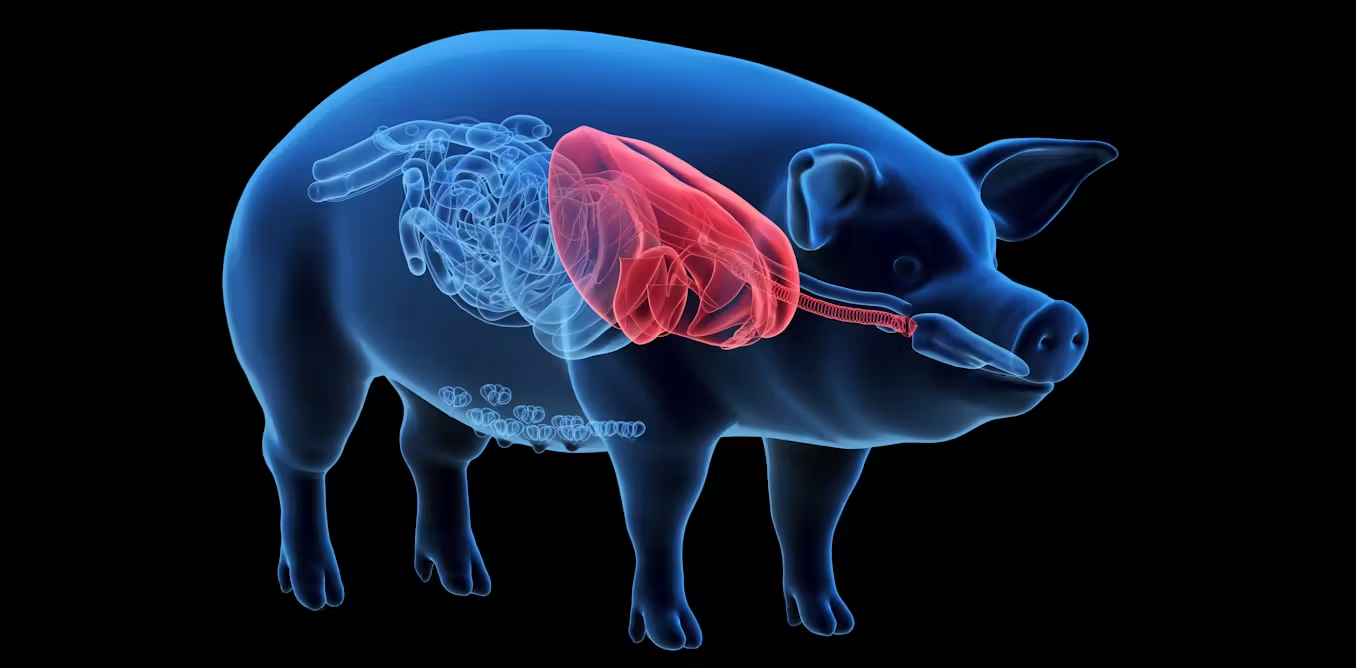
Xenotransplantation: and the pig?
Xenotransplantation in humans is the subject of one announcement after another. This involves transplanting an organ or tissue from a genetically modified animal into a human, to alleviate the shortage of human organs. The “new genomic techniques” are used to genetically modify donor animals. Does the use of these techniques raise new questions of animal ethics?

Self-amplifying messenger RNA “vaccine”: after the human, the duck
A year and a half ago, France made it compulsory to vaccinate farmed ducks against the avian influenza virus, in order to protect its meat and foie gras industries. To date, France is the only country to have taken this vaccination route. One of the two vaccines used, the self-amplifying messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine, raises questions.
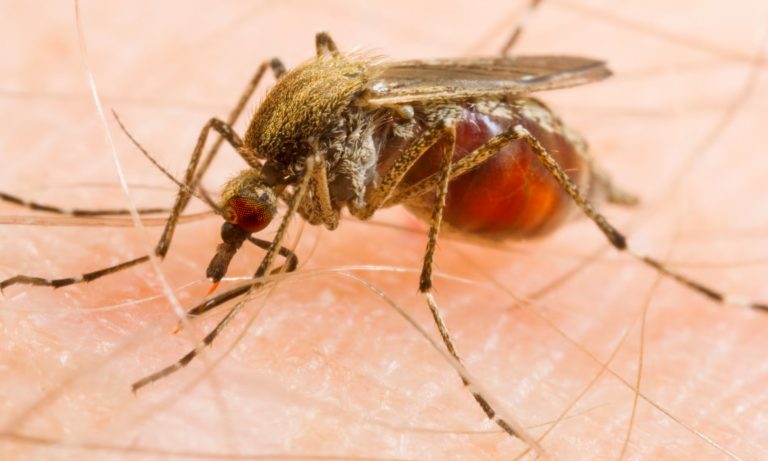

Male mosquitoes genetically modified to produce poison
Mosquitoes carry pathogens that cause diseases such as malaria and dengue fever, and are therefore known as vector-borne diseases. As part of the fight against these mosquitoes, researchers at Macquarie University (Australia) are considering a new genetic strategy. The idea is to genetically modify male mosquitoes so that their sperm produce molecules that will poison female mosquitoes.
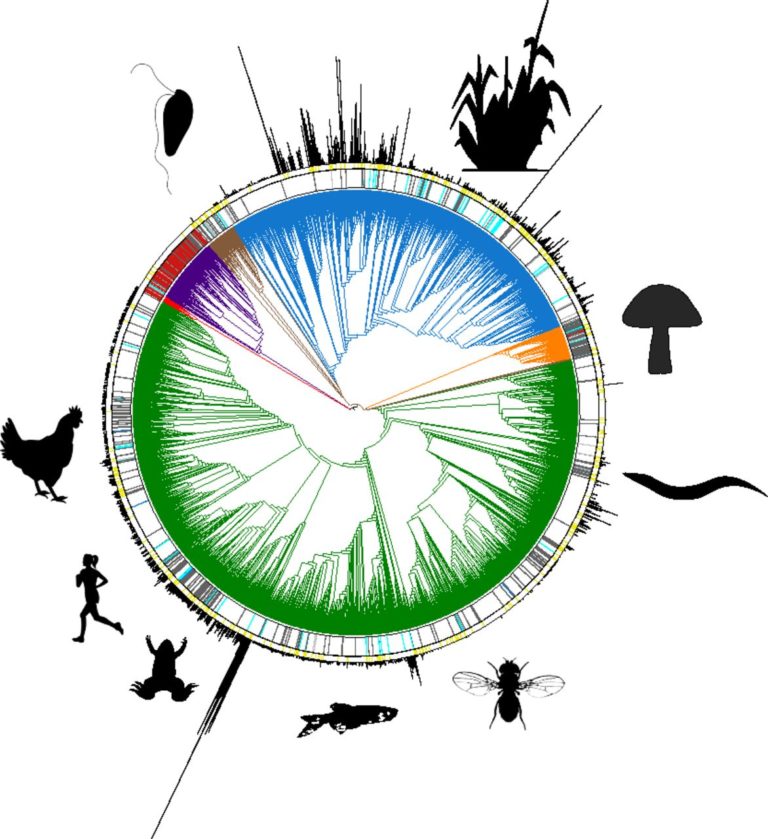

The genome of 1.8 million species is being sequenced
Can biological diversity escape any risk of biopiracy when part of it is digitised in computers? The answer depends on ongoing negotiations within international bodies. In the meantime, an international project to sequence the genome of all known eukaryotic species is making progress. Financed indirectly by players in the IT and artificial intelligence fields, this project even hopes to be able to bypass certain rules thanks to more powerful working tools.

25 years later, insecticidal GMOs face insect resistance
43 detections of insects having acquired resistance to the Bt proteins supposed to kill them were listed in a scientific article in 2023. 43 cases out of 73 studied, i.e. more than half. For the authors of the article, the use of insecticidal GMOs has been crowned with success, as in several cases it has made it possible to reduce or even eradicate local pests. But failures also occurred due to resistance. The authors believe that the future lies in a combination of technologies, among which is RNA interference.

Making salmon sterile… and able to reproduce
In Norway, the Institute of Marine Research (IMR)i has filed a trial application, in 2023, for genetically modified salmon (VIRGIN® salmon). These salmon, bred in cages in the open sea, would be sterile to prevent them from interbreeding with wild populations in the event of accidental dissemination. The Norwegian Environment Agency asked the Norwegian Scientific Committee for Food and the Environment (VKM) to assess the associated environmental risks. VKM’s opinion was highly critical, stating that there was insufficient evidence to consider the trial safeii. In April 2024, after having considered new data, VKM reiterated its negative opinion on this GM salmon trial.
GMO viruses as laboratory tools to be spread in the environment ?
In a recent article, researchers detail several ongoing projects for the genetic modification of viruses. Some of these could be deliberately released into the environment. On February 7, 2024, the European Parliament asked the European Commission to study the potential deregulation of these GMO viruses. A general overview of those projects seems therefore necessary.

Fungicide and herbicide micropeptides on Europe’s doorstep?
Toulouse-based Micropep Technologies has just had one of its fungicidal micropeptides approved in the United States. The technology, developed and patented by this CNRS spin-off, is aiming for European approval by 2030. However, these micropeptides are raising questions about their potential impact on ecosystems.


